Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
If there is a positive productivity shock, then all other things remaining
constant,
a. | the real wage will remain unchanged. | b. | the real wage will rise because workers do not
have to work as hard as before so that labor supply falls. | c. | the real wage will
fall since the marginal product of labor falls. | d. | the real wage will rise. Since labor is more
productive, firms are willing to pay more for it. |
|
|
|
2.
|
According to the Real Business Cycle theory, what fraction of post-World War II
business cycle fluctuations were caused by technology shocks?
|
|
|
3.
|
The Real Business Cycle theory explains involuntary unemployment by assuming
that
a. | labor markets do not clear. | b. | firms enter into wage contracts with
workers. | c. | workers are laid off during recessions. | d. | it is unable to
explain involuntary unemployment. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Real business cycle theory predicts
that
a. | real GDP seldom diverges from its long run
trend. | b. | shocks to long run aggregate supply are the main cause
of instability. | c. | fluctuations in
output are caused by changes in wages and prices. | d. | changes in utility maximising behaviour of consumers causes
instability. |
|
|
|
5.
|
According to real business cycle theory, the main
impulse for the business cycle is
a. | unanticipated changes in aggregate
demand. | b. | adjustments in money growth. | c. | fluctuations in the rate of unemployment. | d. | changes in technology. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Question 6 is based on the following diagram.
The LRAS curves are long run aggregate supply curves and the AD curves are aggregate demand
curves.
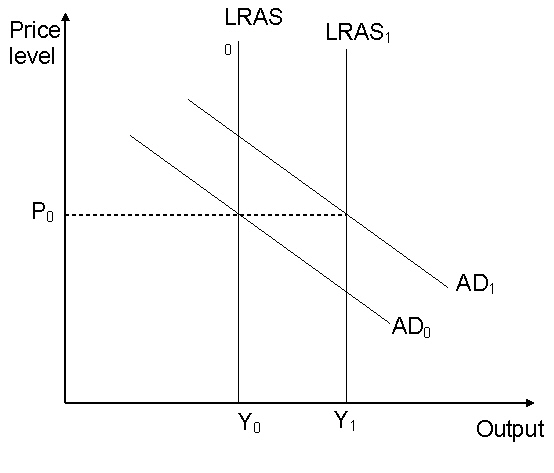
According to real business cycle theory, the
rightward shift in the LRAS curve from LRAS0 to LRAS1
a. | will lead to increased demand for labour and a long run
rise wage costs. | b. | could have been
caused by a positive demand side shock. | c. | would lead to a
subsequent increase in aggregate demand from AD0
toAD1. | d. | is unsustainable
and aggregate supply will fall back to its previous trend
rate. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Real business cycle models of the economy are
consistent with all of the following except
a. | wages and prices which are
sticky. | b. | market clearing models of the
economy. | c. | expectations being formed
rationally. | d. | utility maximising
behaviour by consumers. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The New Keynesian theory of the business cycle
suggests that wages adjust slowly because
a. | wages are determined by the level of
unemployment. | b. | trade unions have
limited bargaining power. | c. | firms operate in
perfectly competitive markets. | d. | negotiations over
wages take place only periodically. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Firms might pay efficiency wages for all of the
following reasons except
a. | to discourage shirking. | c. | to encourage worker retention. | b. | to avoid industrial action. | d. | to reduce training
costs. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Menu costs are the costs of
a. | adjusting prices. | b. | unexpected increases in a range of costs. | c. | employing additional workers. | d. | increasing sales in new markets. |
|