Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which item is least likely to be used to define diversity?
a. | Valuing, respecting, and appreciating differences | b. | Homogeneous,
ethnocentric group | c. | Heterogeneity of attitudes | d. | All the ways in
which we differ
|
|
|
|
2.
|
When a person or group believes their culture to be superior to the other
culture, they are said to be
a. | polycentric | c. | ethnocentric | b. | diverse | d. | egocentric |
|
|
|
3.
|
Identify the two important processes involved in social identity
formation
a. |
Self-categorization & perception |
c. |
Social comparison &
perception |
b. |
Self-categorization & social comparison |
d. |
Self-categorization & stereotyping
|
|
|
|
4.
|
We often rely on a single striking characteristic such as nationality, how
someone may dress, their posture to make judgements about them - when we meet or consider
other people we tend to make judgements about them in a short period of time - this is described as
a. |
The halo effect |
c. | Habituation | b. |
Ethnocentrism |
d. | Prejudice |
|
|
|
5.
|
What are the two main sub processes of the perceptual process?
a. | Habituation and the halo effect | b. | Generalisation and
stereotyping | c. | Interpretation and making sense | d. | Selective attention and perceptual
organisation |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which statement is least true?
a. |
In the early stages of the perceptual process there is a reduction in information
received from our senses |
b. |
The early stages of the perceptual process are
best described as top down processes |
c. |
Later in the perceptual process the brain uses
a variety of mechanisms to fill in any gaps and make sense of the incoming sensory
data |
d. |
The real world is sensed through our sight, taste, smell, hearing and touch - acting
as a stimulus |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following statements, associated with attribution theory, are least
correct?
a. | Attribution is the process of attaching causes or reasons to the actions and
events we see. | b. | Typically when things go right for us we believe it to be a result of the
circumstances | c. | In some cases we determine ourselves or the person to be the cause (internal
causality) | d. |
In some cases we attribute an aspect of the environment (external causality) as the
cause |
|
|
|
8.
|
In their model of Cross cultural competence in international business, Johnson,
Lenartowicz and Apud (2006) discuss three dimensions or antecedents of cultural competence - select
the item that is not one of those dimensions
a. |
Managerial experience |
c. |
Personal skills |
b. |
Personal attributes |
d. |
Cultural
knowledge |
|
|
|
9.
|
Earley and Mosakowski (2004) identify six cultural intelligence profiles -
identify the item not in their list
a. | The ‘Provincial’ | e. | The ‘Analyst’
| b. | The ‘Patriot’ | f. | The ‘Natural’
| c. | The ‘Chameleon’ | g. | The
‘Ambassador’ | d. | The ‘Mimic’
|
|
|
|
10.
|
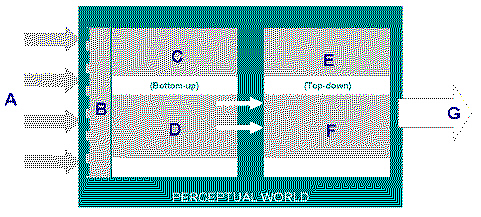 Consider The process of Perception depicted in the
diagram above. Select the text that is represented by the letter “C” in the
diagram a. | Stimulus | d. | Perceptual organization | b. | Habituation/ Halo
effect | e. | Response | c. | Generalisation/ Stereotypes | f. | Selective
Attention |
|
|
|
11.
|
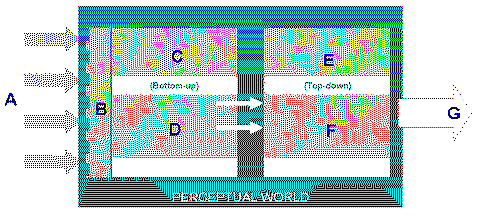 Consider The process of Perception depicted in the
diagram above. Select the text that is represented by the letter “F” in the
diagram a. | Stimulus | d. | Perceptual organization | b. | Habituation/ Halo
effect | e. | Response | c. | Generalisation/ Stereotypes | f. | Selective
Attention |
|
|
|
12.
|
Milliken and Martins (1996) identified common patterns in the processes by which
diversity affected individual, group, and organizational outcomes. Select the item that was NOT
identified by Milliken and Martins (1996)
a. |
Diversity in observable attributes has consistently been found to have negative
effects on affective outcomes |
b. |
The more similar people are in background
variables such as socioeconomic status or attitudes, the more attracted they are likely to be to each
other, at least initially, a phenomenon that when observed in friendship patterns is called
homophily bias. |
c. |
Greater negative effects have been found for
diversity on age than for diversity on race and gender |
d. |
Supervisors appear
to prefer subordinates who have similar organizational tenure and give them higher performance
ratings |
|
|
|
13.
|
Select the least true statement
a. |
Findings suggest that individuals who are different in racial or ethnic background
tend to be less psychologically committed to their organizations, less inclined to stay with the
organization, and more likely to be absent |
b. |
Groups that were homogeneous with respect
to the ethnic backgrounds of their members produced higher quality ideas in a brainstorming task than
more heterogeneous groups did |
c. |
Research on racial differences in performance
ratings by supervisors indicated that black people were generally rated lower than white people by
supervisors |
d. |
New black recruits tend to be assigned to black supervisors
|
|
|
|
14.
|
Select the least true statement
a. | A negotiation is a discussion intended to produce an agreement and possibly
resolve a conflict | b. |
Conflict (dispute) resolution negotiations
involve parties that seek to overcome something that is blocking goal attainment |
c. | Negotiations and
decision-making are both intertwined and culture bound. | d. | Transactional
negotiation involves buyers and sellers negotiating terms | e. |
Typical stages
within the negotiation process include preparation, relationship building, information exchange,
persuasion, concession and agreement |
f. |
There is a well documented uni-cultural
approach to negotiation |
|
|
|
15.
|
Studies have provided support for the idea that racial diversity benefits
decision making; for example, Watson, Kumar, and Michaelsen (1993) studied for “X” weeks
the interaction and performance of culturally homogeneous and culturally diverse groups. They
reported that homogeneous groups initially scored higher on both process and performance
effectiveness. Over time, both types of groups showed improvement on process and performance, and the
between-groups differences lessened. By week “X”, there were no differences in process or
overall performance, but the heterogeneous groups scored higher on two task measures (range of
perspectives and alternatives generated).
What is the value of X?
|