True/False
Indicate whether the
sentence or statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
Economic models must mirror reality or they are of
no value.
|
|
|
2.
|
Assumptions make the world easier to understand
because they simplify reality and focus our attention.
|
|
|
3.
|
It is reasonable to assume that the world is
composed of only one person when modelling international trade.
|
|
|
4.
|
When people act as scientists, they must try to be
objective.
|
|
|
5.
|
If an economy is operating on its production
possibilities frontier, it must be using its resources efficiently.
|
|
|
6.
|
If an economy is operating on its production
possibilities frontier, it must produce less of one good if it produces more of
another.
|
|
|
7.
|
Points outside the production possibilities
frontier are attainable but inefficient.
|
|
|
8.
|
If an economy were experiencing substantial
unemployment, the economy is producing inside the production possibilities frontier.
|
|
|
9.
|
The production possibilities frontier is bowed
outward because the trade-offs between the production of any two goods are constant.
|
|
|
10.
|
An advance in production technology would cause the
production possibilities curve to shift outward.
|
|
|
11.
|
Macroeconomics is concerned with the study of how
households and firms make decisions and how they interact in specific markets.
|
|
|
12.
|
The statement, "An increase in inflation tends
to cause unemployment to fall in the short run," is normative.
|
|
|
13.
|
When economists make positive statements, they are
more likely to be acting as scientists.
|
|
|
14.
|
Normative statements can be refuted with
evidence.
|
|
|
15.
|
Most economists believe that tariffs and import
quotas usually reduce general economic welfare.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
The scientific method requires that
a. | the scientist be objective. | b. | the scientist use precision equipment. | c. | only correct theories are tested. | d. | only incorrect theories are tested. | e. | the scientist use test tubes and have a clean
lab. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is most likely to produce
scientific evidence about a theory?
a. | A lawyer employed by Renault addressing the impact of
air bags on passenger safety. | b. | An economist
permanently employed at a leading university analysing the impact of bank regulations on lending to
small businesses. | c. | An economist
employed by the Trades Union Congress doing research on the impact of trade policy on workers'
wages. | d. | A radio talk show host collecting data from listeners on
how capital markets respond to taxation. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following statements regarding the
circular-flow diagram is true?
a. | If Susan works for BAe Systems and receives a salary
payment, the transaction takes place in the market for goods and services. | b. | If BAe Systems sells a military aircraft, the transaction takes place in the
market for factors of production. | c. | None of these
answers. | d. | The factors of production are owned by
households. | e. | The factors of
production are owned by firms. |
|
|
|
19.
|
In which of the following cases is the assumption
most reasonable?
a. | To address the impact of taxes on income distribution,
an economist assumes that everyone earns the same income. | b. | To address the impact of money growth on inflation, an economist assumes that
money is strictly coins. | c. | To model the
benefits of trade, an economist assumes that there are two people and two
goods. | d. | To estimate the speed at which a beach ball falls, a
physicist assumes that it falls in a vacuum. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Economic models are
a. | usually made of wood and
plastic. | b. | built with assumptions. | c. | useless if they are simple. | d. | created to duplicate reality. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following is not a factor of
production?
a. | labour | b. | land | c. | money | d. | capital | e. | All of these
answers are factors of production. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Points on the production possibilities frontier
are
a. | inefficient. | b. | normative. | c. | unattainable. | d. | efficient. | e. | none of these
answers. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following will not shift a
country's production possibilities frontier outward?
a. | an advance in technology | b. | an increase in the labour force | c. | an increase in the capital stock | d. | a reduction in unemployment |
|
|
|
24.
|
Economic growth is depicted by
a. | a shift in the production possibilities frontier
outward. | b. | a movement from inside the curve toward the
curve. | c. | a shift in the production possibilities frontier
inward. | d. | a movement along a production possibilities frontier
toward capital goods. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Refer to Exhibit 6. If the economy is operating at
point C, the opportunity cost of producing an additional 15 units of bacon is
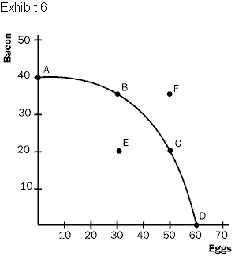
a. | 40 units of eggs. | b. | 10 units of eggs. | c. | 20 units of
eggs. | d. | 30 units of eggs. | e. | 50 units of eggs. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Refer to Exhibit 6. If the economy were operating
at point E,
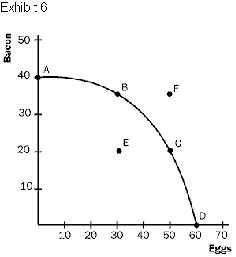
a. | the opportunity cost of 20 additional units of eggs is
10 units of bacon. | b. | the opportunity
cost of 20 additional units of eggs is 20 units of bacon. | c. | the opportunity cost of 20 additional units of eggs is 30 units of
bacon. | d. | 20 additional units of eggs can be produced with no
impact on bacon production. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Refer to Exhibit 6. Point F represents
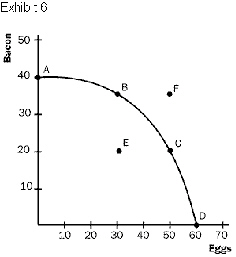
a. | none of these answers. | b. | a combination of production that can be reached if we reduce the production of
eggs by 20 units. | c. | a combination of
production that can be reached if there is a sufficient advance in
technology. | d. | a combination of
production that is inefficient because there are unemployed
resources. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Refer to Exhibit 6. As we move from point A to
point D,
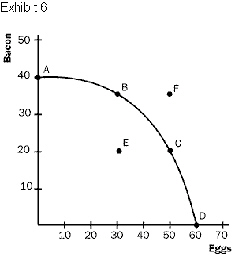
a. | the opportunity cost of eggs in terms of bacon
falls. | b. | the opportunity cost of eggs in terms of bacon
rises. | c. | the opportunity cost of eggs in terms of bacon is
constant. | d. | the economy becomes less
efficient. | e. | the economy
becomes more efficient. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following issues is related to
microeconomics?
a. | the impact of oil prices on car
production | b. | the impact of
money on inflation | c. | the impact of
technology on economic growth | d. | the impact of the
deficit on saving |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following statements about
microeconomics and macroeconomics is not true?
a. | The study of very large industries is a topic within
macroeconomics. | b. | Macroeconomics is
concerned with economy-wide phenomena. | c. | Microeconomics is
a building block for macroeconomics. | d. | Microeconomics and
macroeconomics cannot be entirely separated. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following statements is
normative?
a. | Large government deficits cause an economy to grow more
slowly. | b. | People work harder if the wage is
higher. | c. | The unemployment rate should be
lower. | d. | Printing too much money causes
inflation. |
|
|
|
32.
|
In making which of the following statements is an
economist acting more like a scientist?
a. | A reduction in unemployment benefits will reduce the
unemployment rate. | b. | The rate of
inflation should be reduced because it robs the elderly of their savings. | c. | The unemployment rate should be reduced because unemployment robs individuals
of their dignity. | d. | The state should
increase subsidies to universities because the future of our country depends on
education. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Positive statements are
a. | macroeconomic. | b. | microeconomic. | c. | statements of
description that can be tested. | d. | statements of
prescription that involve value judgments. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Suppose two economists are arguing about policies
that deal with unemployment. One economist says, "The government should fight unemployment
because it is the greatest social evil." The other economist responds, "Nonsense! Inflation
is the greatest social evil." These economists
a. | really don't disagree at all. It just appears that
they disagree. | b. | disagree because
they have different values. | c. | none of these
answers | d. | disagree because they have different scientific
judgments. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Suppose two economists are arguing about policies
that deal with unemployment. One economist says, "The government could lower unemployment by one
percentage point if it would just increase government spending by 50 billion dollars." The other
economist responds, "Nonsense and poppycock! If the government spent an additional 50 billion
dollars, it would reduce unemployment by only one tenth of one percent, and that effect would only be
temporary!" These economists
a. | none of these answers | b. | disagree because they have different scientific
judgments. | c. | really don't
disagree at all. It just appears that they disagree. | d. | disagree because they have different
values. |
|