True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
The largest source of revenue for the UK government is personal income
tax.
|
|
|
2.
|
An excise tax is a tax on income.
|
|
|
3.
|
Expenditure on national defence is an example of a government transfer
payment.
|
|
|
4.
|
To judge the vertical equity of a tax system, one should look at the average tax
rate of taxpayers of differing income levels.
|
|
|
5.
|
The marginal tax rate is the appropriate tax rate to judge how much a particular
tax system distorts economic decision making.
|
|
|
6.
|
A lump-sum tax is a progressive tax.
|
|
|
7.
|
Lump-sum taxes are equitable but not efficient.
|
|
|
8.
|
An efficient tax is one that generates minimal deadweight losses and minimal
administrative burdens.
|
|
|
9.
|
The personal income tax system in the United Kingdom is regressive.
|
|
|
10.
|
Corporations bear the burden of corporation tax.
|
|
|
11.
|
A tax system with a low marginal tax rate generates less deadweight loss and is
more efficient than a similar tax system with a higher marginal tax rate.
|
|
|
12.
|
If the government runs a budget deficit, it means that there is an excess of
government spending over government receipts.
|
|
|
13.
|
Reducing tax rates can lead to an increase in tax revenue for a
government.
|
|
|
14.
|
The marginal tax rate is total taxes paid divided by total income.
|
|
|
15.
|
The chief advantage of replacing personal income tax with a consumption tax is
that it would remove the disincentive to saving that arises from the levying of personal income tax
on income from savings.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following lists the sources of tax revenue to the UK government
from the largest source to the smallest source?
a. | national insurance contributions, personal income tax, value added
tax. | b. | personal income tax, national insurance contributions, value added
tax. | c. | personal income tax, value added tax, national insurance
contributions. | d. | value added tax, personal income tax, national insurance
contributions. |
|
|
|
17.
|
In the United Kingdom, the tax system is
a. | lump sum. | c. | progressive. | b. | regressive. | d. | proportional. |
|
|
|
18.
|
In 2008-09, the total amount of taxes levied in the UK was equivalent to around
which of the following for every man, woman and child in the country (to the nearest thousand)
a. | £5,000. | b. | £6,000. | c. | £7,000. | d. | £8,000. | e. | £9,000. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following lists the spending by the UK government from the largest
category to the smallest category?
a. | defence, National Health Service, Social Security, education, transport, pubic order
and safety. | b. | Social Security, defence, National Health Service, transport, pubic order and
safety. | c. | Social Security, National Health Service, education, defence, pubic order and safety,
transport. | d. | National Health Service, defence, education, Social Security, transport, pubic order
and safety. |
|
|
|
20.
|
If the German government runs a budget surplus, there is
a. | an excess of government receipts over government spending. | b. | an equality of
government spending and receipts. | c. | a surplus of government
workers. | d. | an excess of government spending over government
receipts. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Heike values a pair of blue jeans at €40. If the price is €35, Heike
buys the jeans and generates consumer surplus of €5. Suppose a tax is placed on blue jeans that
causes the price of blue jeans to rise to €45. Now Heike chooses not to buy a pair of jeans.
This example has demonstrated
a. | the deadweight loss from a tax. | b. | the ability-to-pay
principle. | c. | the benefits principle. | d. | horizontal equity. | e. | the administrative
burden of a tax. |
|
|
|
22.
|
A tax for which high income taxpayers pay a smaller fraction of their income
than do low income taxpayers is known as
a. | a proportional tax. | c. | an equitable tax. | b. | a regressive tax. | d. | a progressive
tax. |
|
|
|
23.
|
An efficient tax
a. | minimizes the administrative burden from the tax. | b. | does all of the
things described in these answers. | c. | raises revenue at the smallest possible cost to
taxpayers. | d. | minimizes the deadweight loss from the tax. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The marginal tax rate is
a. | the taxes paid by the marginal worker. | b. | total income divided by total taxes
paid. | c. | the extra taxes paid on an additional unit of income. | d. | total taxes paid
divided by total income. |
|
|
|
25.
|
The appropriate tax rate to consider to judge the vertical equity of a tax
system is the
a. | marginal tax rate. | c. | horizontal tax rate. | b. | average tax rate. | d. | proportional tax
rate. |
|
|
|
26.
|
The average tax rate is
a. | total taxes paid divided by total income. | b. | the extra taxes paid
on an additional dollar of income. | c. | the taxes paid by the marginal
worker. | d. | total income divided by total taxes paid. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following taxes is the most efficient tax?
a. | a consumption tax | c. | a progressive income tax | b. | a lump-sum
tax | d. | a proportional income
tax |
|
|
|
28.
|
A progressive tax system is one where
a. | marginal tax rates are high. | b. | higher income taxpayers pay more taxes than do
lower income taxpayers. | c. | marginal tax rates are low. | d. | higher income
taxpayers pay a greater percentage of their income in taxes than do lower income
taxpayers. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Refer to Table 12.10. The average tax rate for a German taxpayer earning
€40,000 (rounded up) is 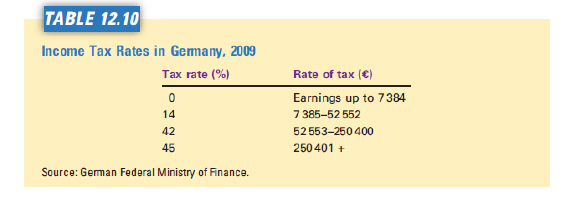 a. | 0 percent. | b. | 5 per cent | c. | 7 per
cent | d. | 12 per cent | e. | 14 per cent |
|
|
|
30.
|
Refer to Table 12.10. This tax system is 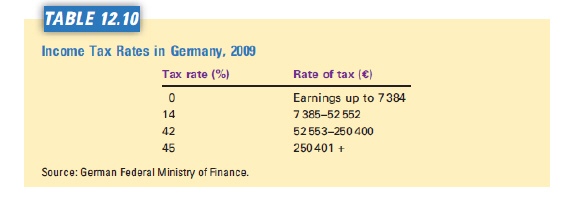 a. | regressive. | c. | lump-sum. | b. | proportional. | d. | progressive |
|
|
|
31.
|
Refer to Table 12.10. The marginal tax rate for a taxpayer whose earnings rises
from €50,000 to €60,000 is 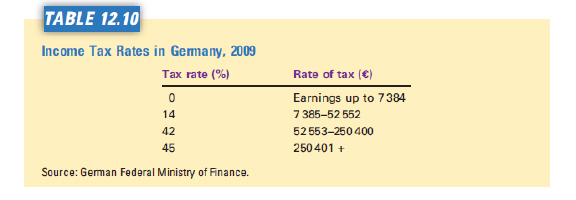 a. | 0 percent. | b. | 50 percent. | c. | 100
percent. | d. | 150 percent. | e. | 200 per cent |
|
|
|
32.
|
The ability-to-pay principle of taxation suggests that if a tax system is to be
vertically equitable, it should be
a. | efficient. | b. | progressive. | c. | regressive. | d. | proportional. | e. | lump-sum. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following taxes can be supported by the benefits principle of
taxation?
a. | All of these answers can be supported by the benefits principle of
taxation. | b. | progressive income taxes used to pay for national defence | c. | petrol taxes used to
pay for roads | d. | property taxes used to pay for police and the court system | e. | progressive income
taxes used to pay for antipoverty programs |
|
|
|
34.
|
The appropriate tax rate to consider to gauge how much the tax system distorts
incentives and decision making is the
a. | proportional tax rate. | b. | average tax rate. | c. | marginal tax
rate. | d. | vertical tax rate. | e. | horizontal tax
rate. |
|
|
|
35.
|
A tax system is regarded as horizontally equitable if
a. | all taxpayers pay the same amount of tax | b. | taxes on all goods
are levied at the same rate | c. | taxes are as low as
possible | d. | the system comprises only lump sum taxes | e. | taxpayers with
similar abilities to pay taxes pay the same amount |
|