True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which few firms sell similar
products.
|
|
|
2.
|
Similar to firms in perfectly competitive markets, firms in monopolistically
competitive markets can enter and exit the market without restriction so profits are driven to zero
in the long run.
|
|
|
3.
|
In the long run, firms in monopolistically competitive markets produce at the
minimum of their average total cost curves.
|
|
|
4.
|
Similar to a monopolist, a monopolistically competitive firm faces a
downward-sloping demand curve for its product.
|
|
|
5.
|
Both monopolists and monopolistically competitive firms produce the quantity at
which marginal revenue equals marginal cost and then use the demand curve facing the firm to
determine the price consistent with that quantity.
|
|
|
6.
|
Since a monopolistically competitive firm charges a price that exceeds marginal
cost, the firm fails to produce some units that the buyers value in excess of the cost of production
and, thus, monopolistic competition is inefficient.
|
|
|
7.
|
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm charges a price that
exceeds average total cost.
|
|
|
8.
|
Economists generally agree that monopolistically competitive firms should be
regulated in order to increase economic efficiency.
|
|
|
9.
|
Firms that sell highly differentiated consumer products are more likely to spend
a large percentage of their revenue on advertising.
|
|
|
10.
|
Advertising must be socially wasteful because advertising simply adds to the
cost of producing a product.
|
|
|
11.
|
Critics of advertising argue that advertising decreases competition while
defenders of advertising argue that advertising increases competition and reduces prices to
consumers.
|
|
|
12.
|
Even advertising that appears to contain little information about the product
may be useful because it provides a signal about the quality of the product.
|
|
|
13.
|
Brand names allow firms to make economic profits in the long run because they
are able to sell inferior products based on the apparent connection of those products to the
firm's unrelated high quality products.
|
|
|
14.
|
Monopolistic competition is called this because one firm dominates the whole
market and so is able to set prices which all others must follow.
|
|
|
15.
|
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm produces at the efficient
scale while a competitive firm has excess capacity.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a monopolistically competitive
market?
a. | free entry and exit | c. | many sellers | b. | long-run economic profits | d. | differentiated
products |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following products is least likely to be sold in a monopolistically
competitive market?
a. | breakfast cereal | c. | video games | b. | cotton | d. | beer |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following is true regarding the similarities and differences in
monopolistic competition and monopoly?
a. | The monopolist faces a downward-sloping demand curve while the monopolistic
competitor faces an elastic demand curve. | b. | The monopolist charges a price above marginal
cost while the monopolistic competitor charges a price equal to marginal cost. | c. | The monopolist makes
economic profits in the long run while the monopolistic competitor makes zero economic profits in the
long run. | d. | Both the monopolist and the monopolistic competitor operate at the efficient
scale. |
|
|
|
19.
|
In the short run, if the price is above average total cost in a monopolistically
competitive market, the firm makes
a. | losses and firms exit the market. | c. | losses and firms enter the
market. | b. | profits and firms exit the market. | d. | profits and firms enter the
market. |
|
|
|
20.
|
If the monopolistic competitor described by Exhibit 3 is producing at the
profit-maximizing (loss-minimizing) level of output, it 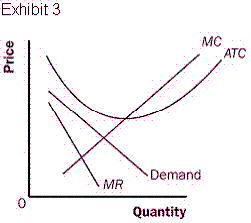 a. | is generating zero profits. | b. | is generating profits. | c. | could be generating
either profits or losses depending on what quantity it chooses to produce. | d. | is generating
losses. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The monopolistically competitive market shown in Exhibit 3 will, in the long
run, 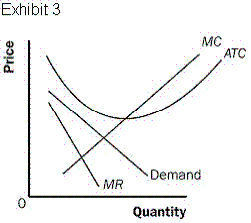 a. | attract new producers into the market, which will shift the demand faced by incumbent
firms to the left. | b. | attract new producers into the market, which
will shift the demand faced by incumbent firms to the right. | c. | cause producers to
exit the market, which will shift the demand faced by incumbent firms to the
left. | d. | cause producers to exit the market, which will shift the demand faced by incumbent
firms to the right. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following is true regarding the production and pricing decisions of
monopolistically competitive firms? Monopolistically competitive firms choose the quantity at which
marginal cost equals
a. | marginal revenue and then use the demand curve to determine the price consistent with
this quantity. | b. | average total cost and then use the supply curve to determine the price consistent
with this quantity. | c. | marginal revenue and then use the supply curve
to determine the price consistent with this quantity. | d. | average total cost and then use the demand
curve to determine the price consistent with this quantity. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Exhibit 4 depicts a monopolistically competitor
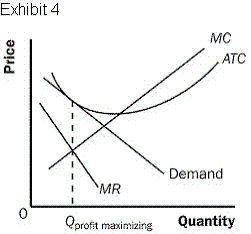 a. | generating normal profits | c. | generating zero profits in the long
run. | b. | generating profits in the short run. | d. | generating losses in the short
run. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following is true with regard to monopolistically competitive
firms' scale of production and pricing decisions? Monopolistically competitive firms
produce
a. | at the efficient scale and charge a price equal to marginal cost. | b. | at the efficient
scale and charge a price above marginal cost. | c. | with excess capacity and charge a price above
marginal cost. | d. | with excess capacity and charge a price equal to marginal
cost. |
|
|
|
25.
|
One source of inefficiency in monopolistic competition is that
a. | since price is above marginal cost, surplus is redistributed from buyers to
sellers. | b. | monopolistically competitive firms earn economic profits in the long
run. | c. | monopolistically competitive firms produce beyond their efficient
scale. | d. | since price is above marginal cost, some units are not produced that buyers value
in
excess of the cost of production and this causes a deadweight
loss. |
|
|
|
26.
|
When firms enter a monopolistically competitive market and the business-stealing
externality is larger than the product-variety externality, then
a. | there are too many firms in the market and market efficiency could be increased if
firms exited the market. | b. | the number of firms in the market is optimal
and the market is efficient. | c. | there are too few firms in the market and
market efficiency could be increased with additional entry. | d. | the only way to
improve efficiency in this market is for the government to regulate it like a natural
monopoly. |
|
|
|
27.
|
The use of the word "competition" in the name of the market structure
called "monopolistic competition" refers to the fact that
a. | there are many sellers in a monopolistically competitive market and there is free
entry and exit in the market just like a competitive market. | b. | monopolistically
competitive firms face a downward-sloping demand curve just like competitive
firms. | c. | monopolistically competitive firms charge prices equal to the minimum of their
average total cost just like competitive firms. | d. | the products are differentiated in a
monopolistically competitive market just like in a competitive
market. |
|
|
|
28.
|
The use of the word "monopoly" in the name of the market structure
called "monopolistic competition" refers to the fact that
a. | monopolistically competitive firms charge prices equal to their marginal costs just
like monopolists. | b. | a monopolistically competitive firm faces a
downward-sloping demand curve for its differentiated product and so does a
monopolist. | c. | monopolistically competitive markets have free entry and exit just like a
monopolistic market. | d. | monopolistically competitive firms produce
beyond their efficient scale and so do monopolists. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following firms is most likely to spend a large percentage of their
revenue on advertising?
a. | the producer of a highly differentiated consumer product | b. | the manufacturer of
an undifferentiated commodity | c. | a perfect competitor | d. | the manufacturer of
an industrial product | e. | the producer of a low quality product that
costs the same to produce as a similar high quality product. |
|
|
|
30.
|
In the UK in 2008, the greatest amount of advertising expenditures was
for
a. | billboards. | c. | commercials on television and radio. | b. | space in newspapers
and magazines. | d. | direct
mail. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following is not put forth as a criticism of advertising and brand
names?
a. | Advertising manipulates people's tastes to create a desire that otherwise would
not exist. | b. | Advertising increases competition, which causes unnecessary bankruptcies and
layoffs. | c. | Advertising increases brand loyalty, causes demand to be more inelastic and, thus,
increases mark-up over marginal cost. | d. | Brand names cause consumers to perceive
differences between goods that do not exist. | e. | Brand names are only relevant to high-priced
products and so exclude other types of products |
|
|
|
32.
|
Expensive television commercials that appear to provide no specific information
about the product being advertised
a. | may be useful because they provide a signal to the consumer about the quality of the
product. | b. | should be banned by regulators because they add to the cost of the product without
providing the consumer with any useful information about the product. | c. | only affect the
buying habits of irrational consumers. | d. | are most likely used by firms that are perfect
competitors. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following is not an argument put forth by economists in support of
the use of advertising? Advertising:
a. | increases competition. | b. | provides information to customers about prices,
new products, and location of retail outlets. | c. | provides a creative outlet for artists and
writers. | d. | provides new firms with the means to attract customers from existing
firms. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Defenders of the use of brand names argue that brand names
a. | all of these answers | b. | are useful even in socialist economies such as
the former Soviet Union. | c. | provide information about the quality of the
product. | d. | give firms incentive to maintain high quality. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following firms has the least incentive to advertise?
a. | a manufacturer of breakfast cereal | b. | a wholesaler of crude oil | c. | a
restaurant | d. | a manufacturer of home heating and air conditioning |
|